LeetCode 141 - Linked List Cycle
題目
題目連結:https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/
給一個 Linked list,判斷有沒有環。
範例說明
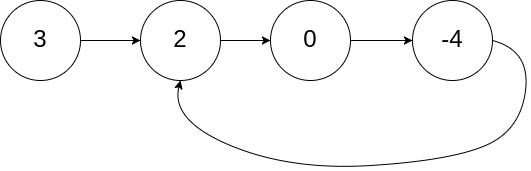
Example 1:
1 | Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 |
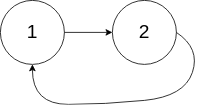
Example 2:
1 | Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0 |
Example 3:
1 | Input: head = [1], pos = -1 |

想法
一般的作法:Time O(N), Space O(N)
有無環的區別就是遍歷 Linked list 時是否會經過重複的位置。
最簡單的想法是使用一個指標 cur 從頭遍歷整個 Linked list,並且將 cur 的記憶體位置都記錄下來(先假設記錄在一個變數 box 內),每次都檢查 box 內有與 cur 相同的記憶體位置。
這個 box 如果是一個陣列,判斷 box 內有與 cur 相同的記憶體位置就需要遍歷整個 box 陣列,會讓整體時間複雜度變為 O(N^2)。
這個 box 可以是一個 Hash table,那麼判斷 box 內有與 cur 相同的記憶體位置 只需要 O(1),整體時間複雜度等於遍歷一遍 Linked list 的時間 O(N)。
C++ box 可以使用 std::unordered_set<ListNode*>,但是要實作 ListNode* 的 compare 函數才能使用。
最佳的作法:Time O(N), Space O(1)
首先,若 Linked list 有環,則一個指標不管走多少步都會被卡在環上一直繞圈。
利用這個性質,使用兩個指標,皆從頭開始遍歷。一個一次走一步,稱之為 slow;另一個一次走兩步,稱之為 fast。可以知道若存在環,不管走多少步,slow 以及 fast 都會一直在環上繞圈,並且因為 fast 每次比 slow 多走一步,所以最後 slow 以及 fast 一定會相會。
時間複雜度的部分,可以知道 slow 以及 fast 在 N 步之內一定會走到環上,並且 fast 每次與 slow 縮減一步的距離,而環的長度小於 N,因此 slow 與 fast 都到達環上後,一定會在 N 步內相會。總時間複雜度為 O(2N) = O(N)。
而沒有環時,fast 會直接走到底,也就是 null。
實作細節
注意迴圈的條件,因為 fast 會一次走兩步,所以有兩個判斷條件: fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr。
至於 slow 因為走的比 fast 還要慢,因此不需要判斷。
程式碼
1 | /** |